Heat loss from uninsulated pipe to air
Heat loss by radiation and convection, step by step calculation guide
Follow us on Twitter ![]()
Question, remark ? Contact us at contact@myengineeringtools.com
| Section summary |
|---|
| 1. Heat losses
through uninsulated pipe |
| 2. Example of heat
loss calculation of uninsulated pipe : Step by Step guide |
| 3. Free Excel calculation tool for uninsulated pipe heat loss : pipe heat loss calculator Excel |
In factories, pipes are typically routed outside. This may not be a problem for most of products and circumstances, but in the case of winter conditions or if the product is sensitive to a loss of temperature, calculating the loss of heat through the insulated pipe is important to check if the temperature of the product is not dropping too much, in which case an insulation would be required.

1. Heat losses through uninsulated pipe
How heat is lost through an uninsulated pipe ?
The heat loss from an uninsulated pipe is basically made of 2 components : the heat loss through radiation and the heat loss through convection.
Total heat loss = radiation heat loss + convection heat loss
1.1 Radiation heat loss
The pipe is emitting heat through radiation. The heat emitted can be calculated thanks to the following formula : Q/A = 0.1713 * ε * [(Ts/100)4 - (Ta/100)4]

With :
Q = heat loss (BTU/h)
A = heat transfer area (ft2)
Ts = surface temperature (R)
Ta = air temperature (R)
ε = emissivity of the pipe
1.2 Convection heat loss
The convection depends on the air velocity (wind speed), there are 2 cases for the calculation, either the wind speed is = 0, or the wind speed is > 0
Natural convection in calm air
The heat loss can be expressed with the following correlation :
Q/A = 0.27*ΔT1.25 / D0.25

With :
Q = heat loss (BTU/h)
A = heat transfer area (ft2)
ΔT = Ts - Ta
Ts = surface temperature (R)
Ta = air temperature (R)
D = pipe diameter (ft)
Convection in the presence of wind
If wind is present, there is a tremendous influence on the heat transfer coefficient which can be estimated the following way : h = 0.11*c*G0.6/D0.4

With :
h = convection heat transfer coefficient (BTU/h.ft2.F)
c = specific heat (BTU/lb/F) = 0.24 for air
G = mass velocity of air (lb/h.ft2) = rho.v
rho = density (lb/ft3) = 0.075 for air
v = wind speed (ft/h)
D = pipe diameter (ft)
1.3 Total loss of heat through uninsulated pipe
The total loss of heat is thus the sum of the heat loss through radiation and the heat loss through convection.
Total heat loss = radiation heat loss + convection heat loss
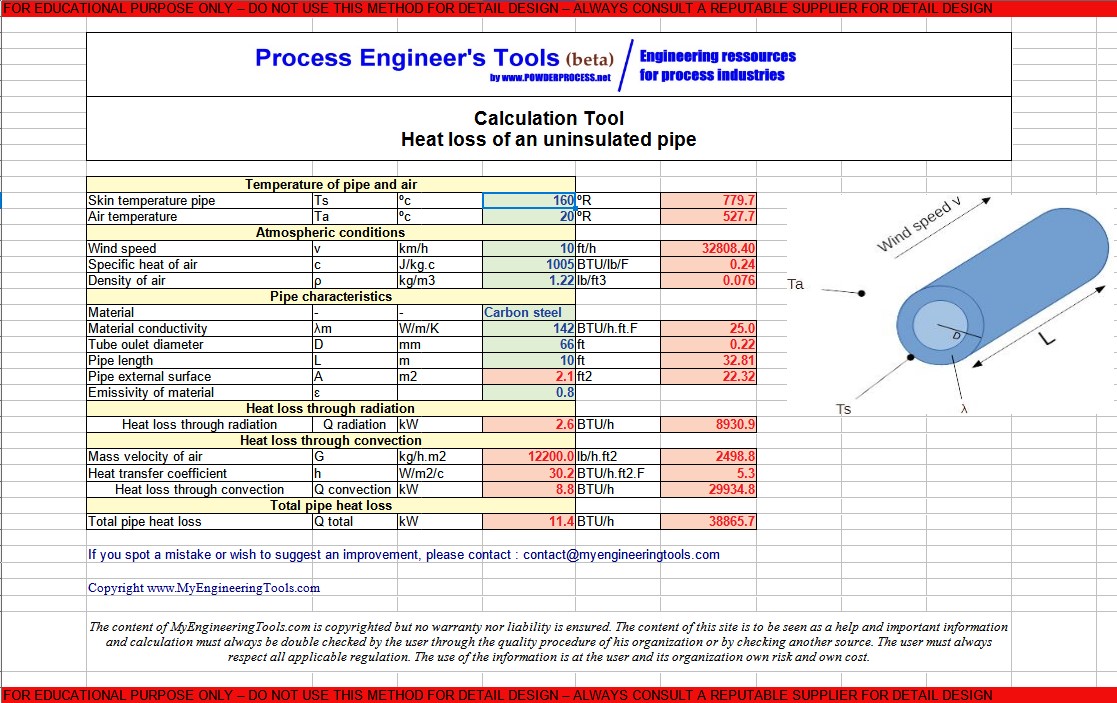
2. Example of heat loss calculation of uninsulated pipe : Step by Step guide
Considering a pipe a 66 mm external diameter and 10 m length that is transporting steam at 160c. What is the heat loss when the pipe is uninsulated, outside, in air at 20c and with wind at 10 km/h.
The pipe is in carbon steel, with an emissivity of 0.8 and a thermal conductivity of 142 W/m.K
It is assumed that the skin temperature of the pipe is equal to the temperature of the fluid, the resistance to heat transfer being on the outside of the pipe.
STEP 1 : Convert to US units
D = 66 mm = 0.2165 ft
L = 10 m = 32.8 ft
Ts = 160c = 320 F = 780 R
Ta = 20c = 68 F = 527.7 R
v = 10 km/h = 32808 ft/h
STEP 2 : Calculate the heat loss due to radiation
The equation given at 1.1 is used to calculate the heat loss due to radiation :
Q radiation = 0.1713*0.8*[(780/100)4 - (527.7/100)4] * 22.32 = 8930.9 BTU/s
With A = Pi*D*L = 22.32 ft2
STEP 3 : Calculate the mass velocity of air
Considering G = mass velocity of air (lb/h.ft2) = rho.v
G = rho.v = 0.075*32808 = 2498.8 lb/h.ft2
STEP 4 : Calculate the heat transfer coefficient by convection
The heat transfer coefficient can be calculated from the correlation given in paragraph 1.3 above :
h = 0.11*c*G0.6/D0.4 = 0.11*0.24*2498.80.6 / 0.220.4 = 5.3 BTU/h.ft2.F
STEP 5 : Calculate the heat loss due to convection
The heat loss due to convection can then be calculated via :
Qconvection = h*A*(Ts - Ta) = 5.3*22.32*(780-527.7) = 29934.8 BTU/h
STEP 6 : Calculate the total heat loss from the uninsulated pipe
Q total = 38865.7 BTU/h (11.4 kW)
3. Free Excel calculation tool for uninsulated pipe heat loss
The heat flux through a pipe or a pipe with insulation can be calculated thanks to this free pipe heat loss calculator Excel : Calculation Tool - heat loss through uninsulated pipe (click here)Source
[Chopey] Handbook of Chemical Engineering calculations, Chopey et al, McGraw Hill, 2004