
Shell - Tube Heat Exchanger : pressure drop on the shell side
How to calculate the pressure drop in the shell of a shell-tube HX ?
Follow us on Twitter ![]()
Question, remark ? Contact us at contact@myengineeringtools.com
| Section summary |
|---|
| 1. Heat transfer on
the tube side of a shell tube heat exchanger |
| 2. Calculation of
the heat transfer coefficient on the tube side |
1. Total pressure drop on the shell side
The pressure drop on the shell side of a shell-tubes heat exchanger is made of several components : the pressure drop in the inlet nozzle, the pressure drop in the outlet nozzle and the pressure drop through the tube bundle in the shell.
ΔPt = ΔPi + ΔPo + ΔPs
With
ΔPt = total pressure drop in the heat exchanger (shell
side)
ΔPi = pressure drop in the inlet nozzle
ΔPo = pressure drop in the outlet nozzle
ΔPs = pressure drop in the shell
The most complex is to calculate the pressure drop in the shell.
2. Pressure drop inside the shell
How to calculate the pressure drop inside the shell of a shell-tubes heat exchanger ?
The Bell Delaware method expresses the pressure drop inside the shell with the following formula :
ΔPs = [(Nch-1).ΔPCTKBP+Nch.ΔPCF].KF+2.ΔPCTKBP.(1+NOF/NCT)
With
ΔPs = pressure drop in the shell (Pa)
Nch = number of baffles
ΔPCT = pressure drop in between 2 baffles for ideal cross
flow (Pa)
ΔPCF = pressure drop in the baffle window section (Pa)
KBP = correction factor for bypass flow
KF = correction factor for leakage in between shell /
baffles and tubes / baffles
NOF = number of tubes in baffle window
NCT = Number of tube rows crossed between baffle tips in
one baffle section
2.1 Pressure drop ΔPCT in cross flow in between 2 baffles
The following equation allows to calculate the pressure drop :
Nu = 1.86.Re1/3.Pr1/3.(di / L)1/3.(μ/μt)0.14

With :
Re = Reynolds number
Pr = Prandtl number = Cp.μ / λ
di = internal diameter of the tube in m
L = length of the tube in m
μ = viscosity of the fluid at bulk temperature in Pa.s (kg/m/s)
μt = viscosity of the fluid a wall temperature in Pa.s
(kg/m/s)
Cp = specific heat of the fluid in J/kg/K (m2/s2/K)
λ = thermal conductivity of the fluid (W/(m.K)) (m⋅kg⋅s−3⋅K−1)
2.2 Turbulent flow (Re > 10000)
The following correlation is from Colburn.
Nu = 0.027.Re0.8.Pr1/3.(μ/μt)0.14

2.3 Calculation of Reynold number
The Reynolds number can be calculated as a function of the mass flow, number of tubes, number of passes, tube diameter.
Re = G.di / μ
G = m / [(Nt/nt).π.di2/4]
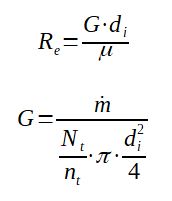
With
G = mass flux in the tube in kg/s/m2
ṁ = mass flow in the heat exchanger on the tube side in kg/s
Nt = number of tubes in the shell tube heat exchanger
nt = number of passes tube in the shell tube heat
exchanger
μ = viscosity of the fluid at bulk temperature in Pa.s (kg/m/s)