
Pipe pressure drop calculation and Excel tools
Pressure drop calculation methodology and free Excel calculation tools
Follow us on Twitter ![]()
Question, remark ? Contact us at contact@myengineeringtools.com
1. Calculation principle : pressure drop in straight pipes, bends / valves...etc... and total pressure drop
2. Calculation tools - Free Excel calculators
1. Calculation principle
The pressure drop in pipes is the sum of the linear pressure drop due to friction with the pipe walls and the singular pressure drop due to the bends, valves...etc... present in the pipePressure drop for straight pipes

Pressure drop due to piping singularities
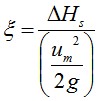 and
and 
Total pressure drop
ΔPT=ΔPf+ΔPSf/2=friction factor, f is Fanning friction factor
DH=Hydraulic diameter in m
um=mean velocity in m/s
ΔPf=pressure drop due to friction in Pa
L=length of pipe in m
ρ=specific gravity in kg/m3
ΔHs=pressure drop due to pipe singularity in m
ΔPs=pressure drop due to pipe singularity in Pa
2. Calculation tools
Please find below some Excel calculation tools for pressure drop in pipes
Pressure
drop Excel calculation tool for incompressible (= liquid) flow
Pressure
drop Excel calculation tool for compressible (= gas) flow, non
choked

FAQ: Pressure Drop Calculation in Piping Systems
1. What is pressure drop in a piping system?
Pressure drop refers to the reduction in pressure within a piping system due to friction between the fluid and the pipe walls, as well as local obstructions (e.g., elbows, valves, or contractions). It is calculated using formulas such as the Darcy-Weisbach equation or the Hagen-Poiseuille equation, depending on the flow regime (laminar or turbulent).
2. How do you calculate pressure drop for laminar flow?
For laminar flow (Re < 2000), pressure drop is calculated using the Hagen-Poiseuille equation: \[ \Delta P = \frac{128 \mu L Q}{\pi d^4} \] Where: - \(\mu\) = dynamic viscosity of the fluid, - \(L\) = pipe length, - \(Q\) = volumetric flow rate, - \(d\) = pipe diameter.
3. What is the difference between linear and singular pressure drop?
Linear pressure drop is caused by continuous friction along the pipe, while singular pressure drop is due to local obstructions like elbows, valves, or contractions. The total pressure drop is the sum of both.
4. How do you use the Darcy-Weisbach equation to calculate pressure drop?
The Darcy-Weisbach equation is used for turbulent flow: \[ \Delta P = \frac{f L \rho v^2}{2 d} \] Where: - \(f\) = friction factor (depends on Reynolds number and pipe roughness), - \(L\) = pipe length, - \(\rho\) = fluid density, - \(v\) = fluid velocity, - \(d\) = pipe diameter.
5. What factors influence pressure drop in a piping system?
Key factors include: - Fluid viscosity and density, - Fluid velocity, - Pipe length and diameter, - Pipe internal roughness, - Presence of singularities (elbows, valves, etc.).
6. How can I reduce pressure drop in a system?
To reduce pressure drop, you can: - Increase pipe diameter, - Reduce fluid velocity, - Minimize the number of singularities, - Use pipes with lower roughness.
7. Are there Excel tools available for pressure drop calculation?
Yes, our page offers free Excel tools for calculating pressure drop, whether for laminar or turbulent flow. These tools account for parameters like length, diameter, viscosity, and fluid velocity.
8. How is the friction factor \(f\) determined in the Darcy-Weisbach equation?
The friction factor \(f\) is determined using the Moody diagram or the Colebrook-White equation, based on the Reynolds number and the relative roughness of the pipe.
9. Why is it important to calculate pressure drop in an industrial system?
Calculating pressure drop is crucial for properly sizing pumps, avoiding overpressure or insufficient flow rates, and optimizing the energy efficiency of the system.
10. Where can I download a pressure drop calculation example?
You can download our free Excel tool directly from this page. It includes practical examples and pre-filled templates to help you get started.
Download
pressure drop for incompressible flow
Download
pressure drop for compressible flow
Top
5 Most Popular
1. Pressure drop
2. Reynolds Number
3.
Pressure drop K coefficients
4. Churchill equation
5. Moody diagram