How to do a For Loop in Python : step by step guide
Follow us on Twitter ![]()
Question, remark ? Contact us at contact@myengineeringtools.com
1. FOR LOOP what it is ?
2. Python FOR LOOP : step by step guide
3. Python FOR LOOP : break instruction
For loops are one of the backbone of any program and Python does not except to the rule. Learn here step by step our to program a FOR LOOP.
1. FOR LOOP what it is ?
A FOR LOOP allows to repeat a defined number of times a set of commands. It is particularly useful to automatize a task in a few lines of codes.
This page is for Python 3 programs.2. Python FOR LOOP : step by step guide
Step 1 : define on which variable you will be iterating and for
how long
The FOR LOOP will be iterating on a variable by updating its value at each pass. Chose your variable and its name to be in line with what the variable must do in the loop and what it is. The key word for a FOR LOOP is simply for (be careful to write lower case only !)
for <name of variable>...
Example :
If the variable is only a counter, something as simple as "i" is a regular choice. On the other hand if you wish to iterate for instance on the names of a list, using "name" can be helpful to better understand the loop function. The start of the loop will then be :
The range of iteration must then be be specified so that Python knows how many time to run the loop. A colon is mandatory at the end of the 1st line of the FOR LOOP.
for <name of variable> in <range> :
Example :
If the iteration must be done over a range of figures, it is
customary to use the range() function where you can specify a
range of figures on which Python will iterate one by one. Note
however that range(i) is iterating until i-1 !
for i in range(10) : --->>> It will iterate from 0 to 9
If the iteration is done over a list, Python allows a very
simple and efficient syntax, just by giving the name of the list,
Python will be able to iterate over it. For example if the list is
defined as names = ['Jean', 'Pierre', 'Emmanuel', 'Kevin']
for name in names : --->>> It will iterate through the names in the list from Jean to Kevin
Top 5 Most
Popular
1. Compressor
Power Calculation
2. Pump Power Calculation
3. Pipe Pressure
Drop Calculation
4. Fluid Velocity in pipes
5. Churchill Correlation
(friction factor)
Step 2 : define the instructions to be executed at each
iteration
After defining the 1st line of the FOR LOOP, then one has just to put below the different instructions of the FOR LOOP. Anything relevant to the program you wish to do is fine but the only convention to respect is to have an indentation ! And when the code in the loop is completed, to remove the indentation !
for <name of variable> in <range> :
<instructions in the loop>
<instructions outside the loop>
Example :
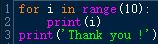
Using the example above, the following code will print all the numbers from 0 to 9 then print only 1 time "Thank you !" :
for i in range(10) :
print(i)
print('Thank you !')

3. Python FOR LOOP : break instruction
Sometimes it is required to get out of the loop early, before all the iteration in the range have been iterated through. It is possible through the break instruction.
When the program encounters a break instruction, it will just stop immediately the loop, and go to the next instruction below which is not indented under the for loop.
Example
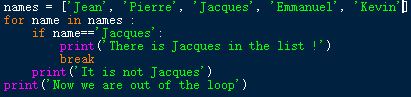
Let's say you want to check if in the list of names, there is the name "Jacques". For example the list is ['Jean', 'Pierre', 'Jacques', 'Emmanuel', 'Kevin']. When you encounter "Jacques", then you want to leave the loop as there is no point continuing reviewing it. This can be written like this :
names = ['Jean', 'Pierre', 'Jacques', 'Emmanuel', 'Kevin']
for name in names :
if name=='Jacques':
print('There is Jacques in
the list !')
break
print('It is not Jacques')
print('Now we are out of the loop')
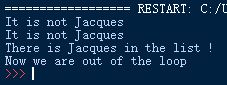
The output will be the following, at the 3rd iteration, we find 'Jacques', thus we leave the loop and 'It is not Jacques' is not printed again.